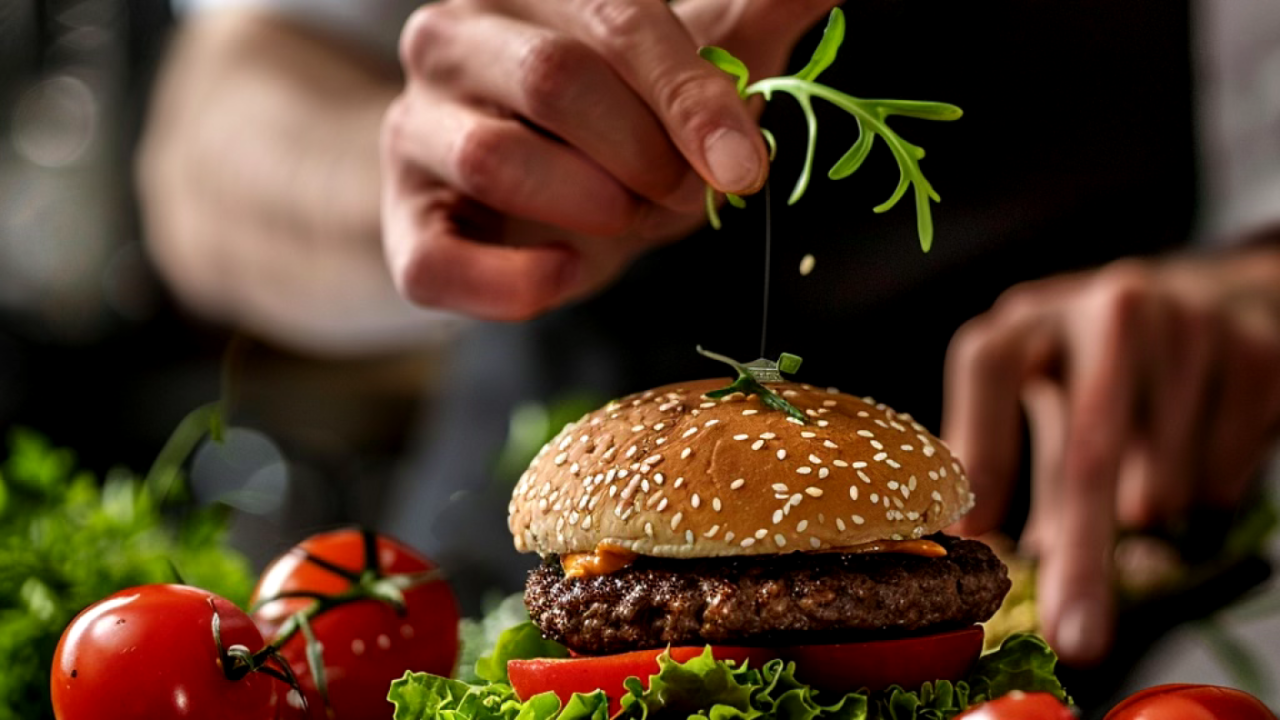
As the global population continues to grow, so does the demand for sustainable and ethical food sources. Lab-grown meat and plant-based alternatives are at the forefront of this culinary revolution, promising to transform the way we eat. These innovations not only aim to provide delicious and nutritious options but also address critical issues like animal welfare, environmental sustainability, and food security.
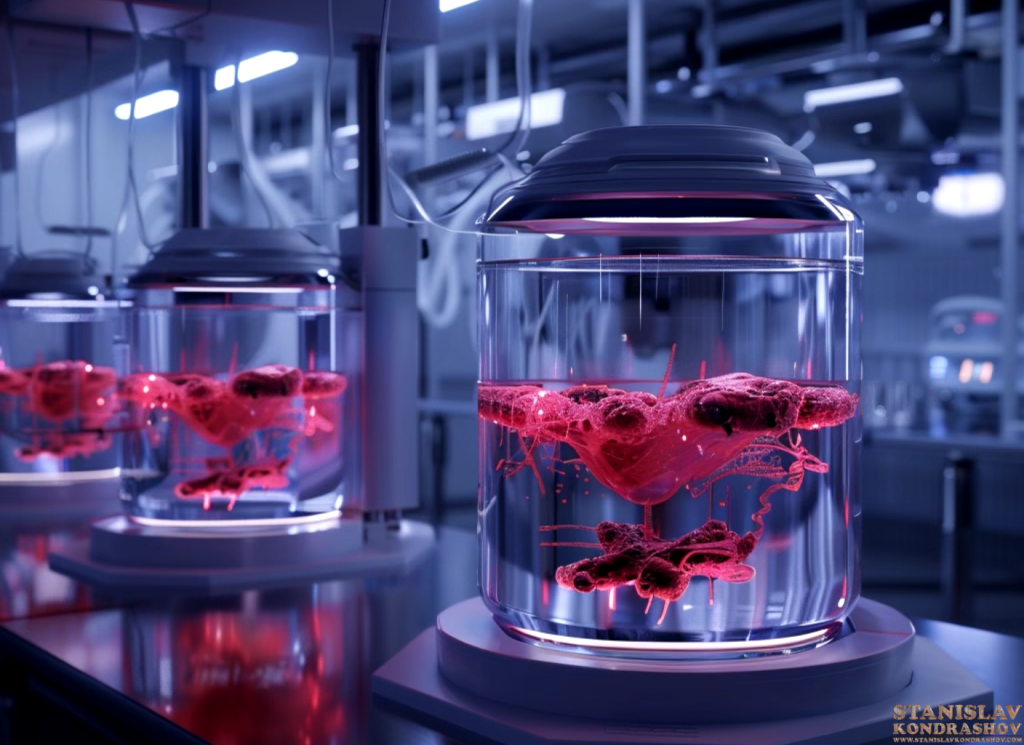

Lab-Grown Meat: A New Frontier
Lab-grown meat, also known as cultured or cell-based meat, is created by culturing animal cells in a controlled environment. This technology allows for the production of real meat without the need to raise and slaughter animals. The process begins with taking a small sample of animal cells, which are then placed in a nutrient-rich culture medium. Over time, these cells grow and multiply, eventually forming muscle tissue that is identical to conventional meat.
The benefits of lab-grown meat are numerous:
- Sustainability: Producing lab-grown meat requires significantly less land, water, and energy compared to traditional livestock farming. This could lead to a drastic reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
- Animal Welfare: Since lab-grown meat does not involve raising and slaughtering animals, it offers a cruelty-free alternative to conventional meat production.
- Health and Safety: The controlled production environment reduces the risk of contamination and the use of antibiotics, making lab-grown meat a potentially safer and healthier option.
Plant-Based Alternatives: A Delicious Evolution
Plant-based alternatives have evolved far beyond traditional vegetarian options. Using innovative food science, companies are creating plant-based products that mimic the taste, texture, and appearance of meat. Ingredients like pea protein, soy, and mushrooms are being transformed into burgers, sausages, and even seafood substitutes.
Key advantages of plant-based alternatives include:
- Environmental Impact: Plant-based foods generally have a much lower environmental footprint compared to meat, requiring less water and land while producing fewer greenhouse gases.
- Health Benefits: Many plant-based products are lower in saturated fats and cholesterol, offering a heart-healthy option for consumers.
- Versatility and Variety: With advancements in food technology, the variety and quality of plant-based options continue to expand, catering to diverse dietary preferences and culinary tastes.

The Road Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities
While the potential of lab-grown meat and plant-based alternatives is vast, several challenges remain. Scaling up production to meet global demand, reducing costs, and gaining consumer acceptance are critical hurdles. Additionally, regulatory approval and labeling standards will play a crucial role in shaping the market.
Despite these challenges, the future of food looks promising. As technology advances and consumer awareness grows, we can expect to see more innovative products that are not only sustainable and ethical but also delicious and accessible.
Lab-grown meat and plant-based alternatives represent a significant shift in our food systems. They offer a glimpse into a future where delicious, nutritious, and sustainable food options are available to all. As these technologies continue to develop, they hold the potential to redefine what we eat and how we think about food.
By Stanislav Kondrashov



